Introduction to Ayurveda: Principles and Practices
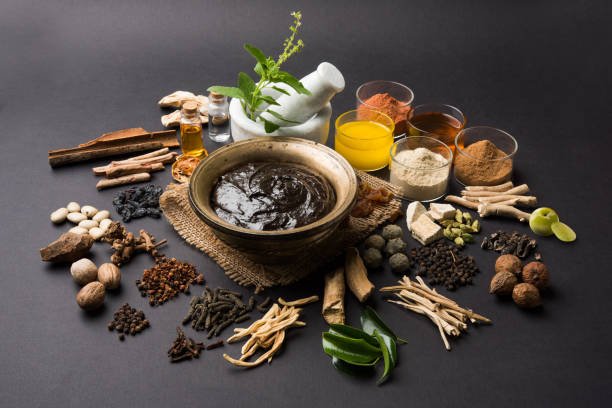

Ayurveda, a holistic healing system that originated in India over 5,000 years ago, emphasizes the balance between the body, mind, and spirit. This ancient practice is rooted in the belief that health is a state of harmony, and it offers a comprehensive approach to wellness through natural remedies, dietary guidelines, and lifestyle changes. In this blog, we will explore the fundamental principles that form the cornerstone of Ayurvedic practice, providing insights into how this time-honored system can enhance our well-being.
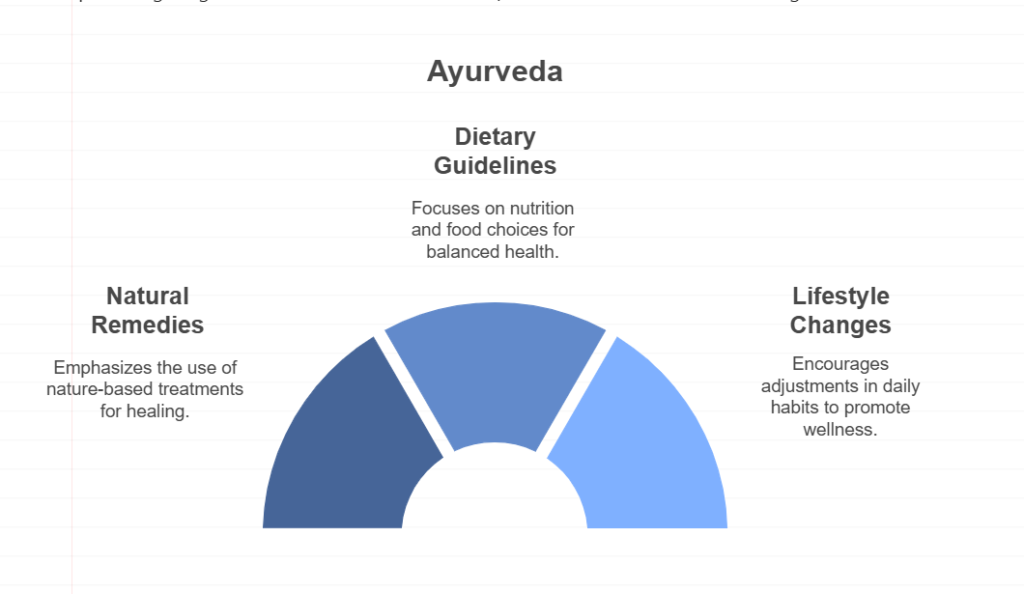
The Core Principles of Ayurveda

1. The Five Elements
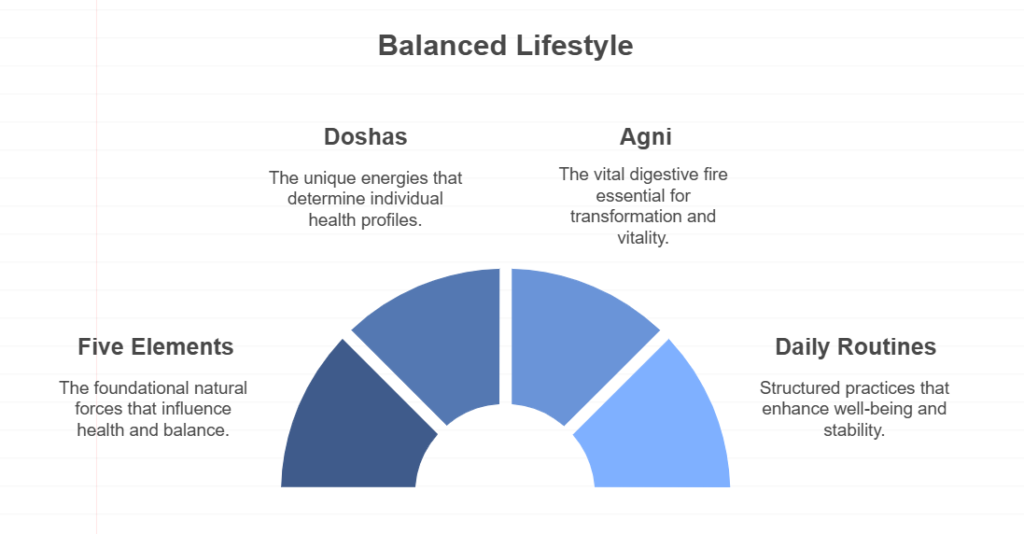
Ayurveda is based on the concept of five fundamental elements: Earth, Water, Fire, Air, and Ether (Space). These elements combine to form three primary energies, known as doshas, which govern our physical and mental characteristics.
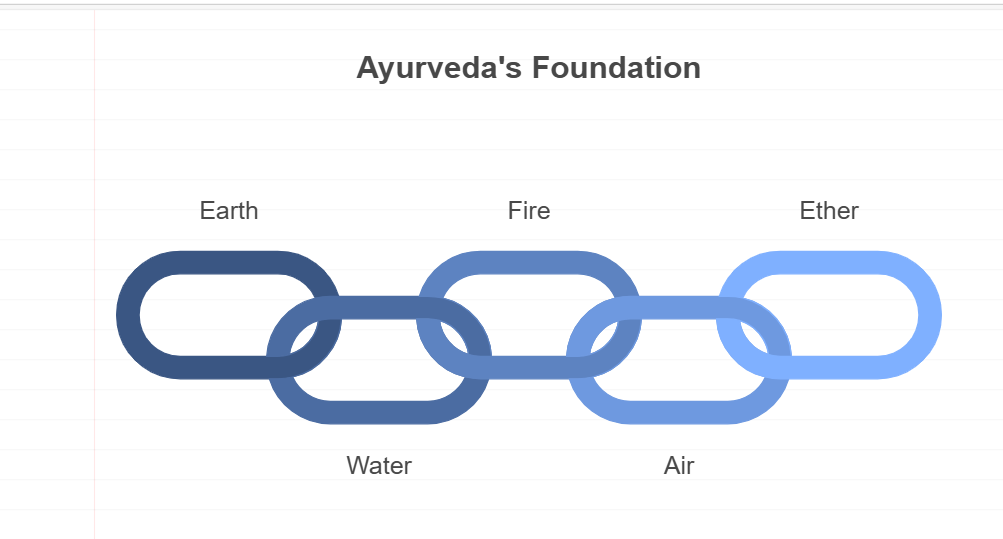
Earth: Represents stability and structure.
Water: Symbolizes fluidity and adaptability.
Fire: Embodies transformation and energy.
Air: Reflects movement and communication.
Ether: Represents space and consciousness.
2. The Three Doshas
The doshas—Vata, Pitta, and Kapha—are the biological energies that influence our physical and emotional health. Each person has a unique combination of these doshas, which determines their constitution (Prakriti) and influences their health and personality.
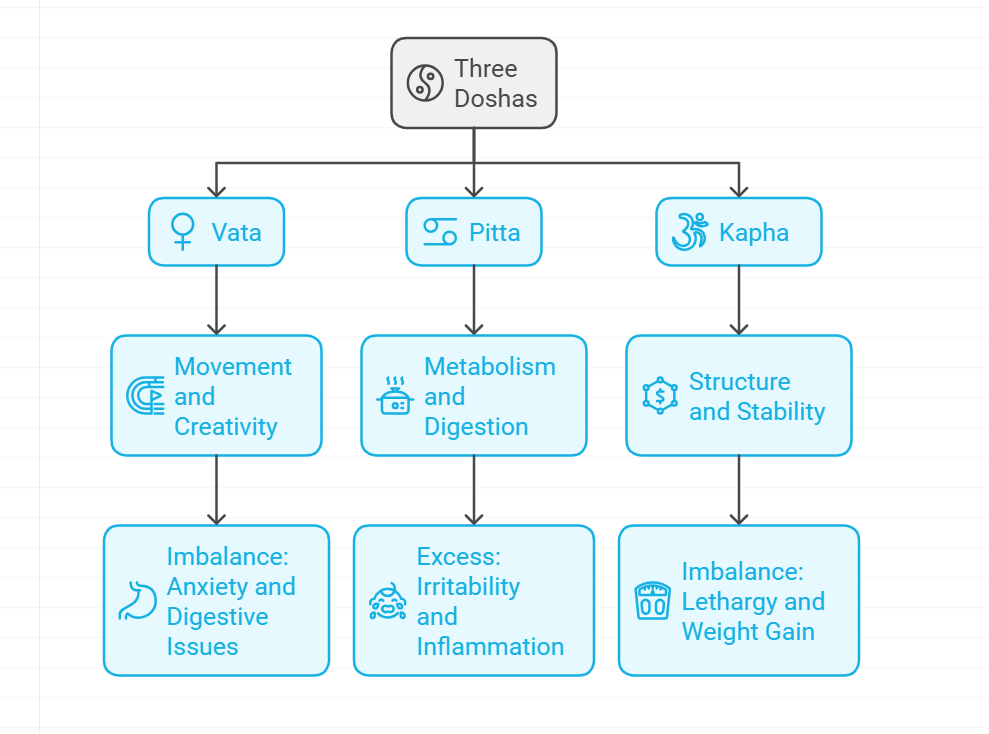
Vata: Composed of Air and Ether, Vata is associated with movement, creativity, and flexibility. Imbalance can lead to anxiety and digestive issues.
Pitta: Made up of Fire and Water, Pitta governs metabolism, digestion, and transformation. An excess can cause irritability and inflammation.
Kapha: Formed from Earth and Water, Kapha provides structure and stability. Imbalance may result in lethargy and weight gain.
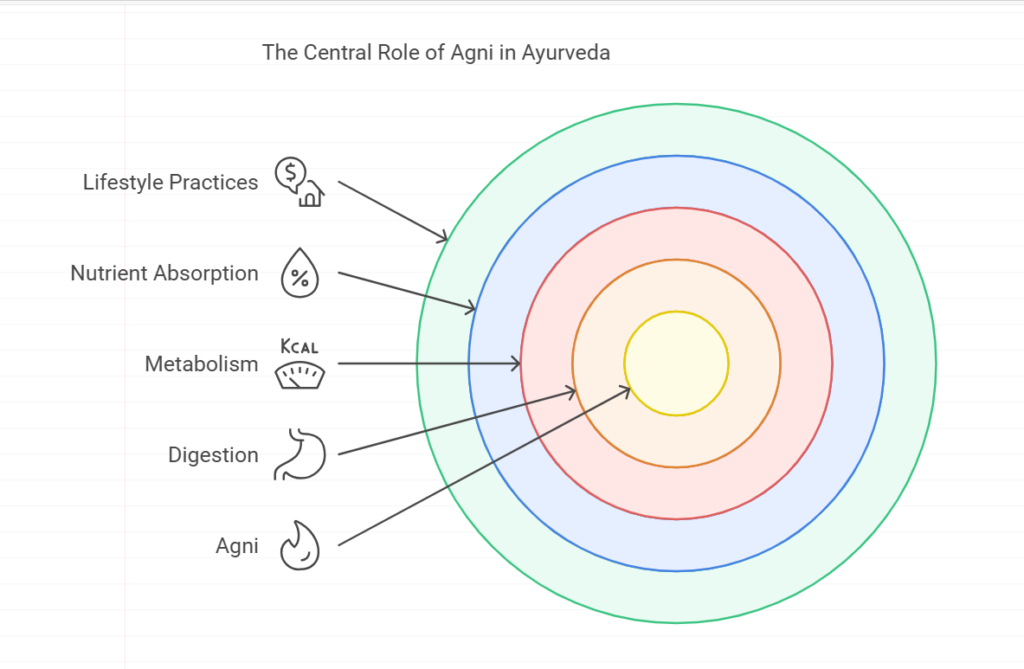
The Concept of Agni
Agni, or digestive fire, is a crucial concept in Ayurveda. It refers to the body’s ability to digest food, thoughts, and experiences. A balanced Agni is essential for optimal health, as it influences metabolism and the absorption of nutrients. Ayurveda emphasizes the importance of maintaining a strong Agni through proper diet, lifestyle, and seasonal adjustments.
4. The Importance of Dinacharya
Dinacharya, or daily routine, is a fundamental aspect of Ayurvedic practice. It encourages individuals to align their daily activities with the natural rhythms of nature, promoting balance and well-being. Key components of Dinacharya include:
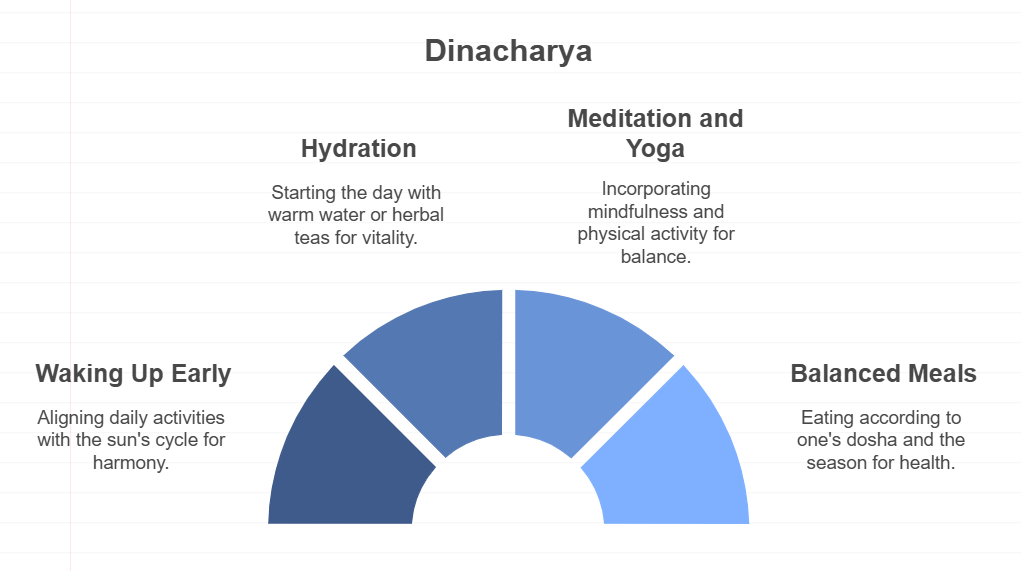
Waking up early: Aligning with the natural cycle of the sun.
Hydration: Starting the day with warm water or herbal teas.
Meditation and Yoga: Incorporating mindfulness and physical activity.
Balanced meals: Eating according to one’s dosha and the season.
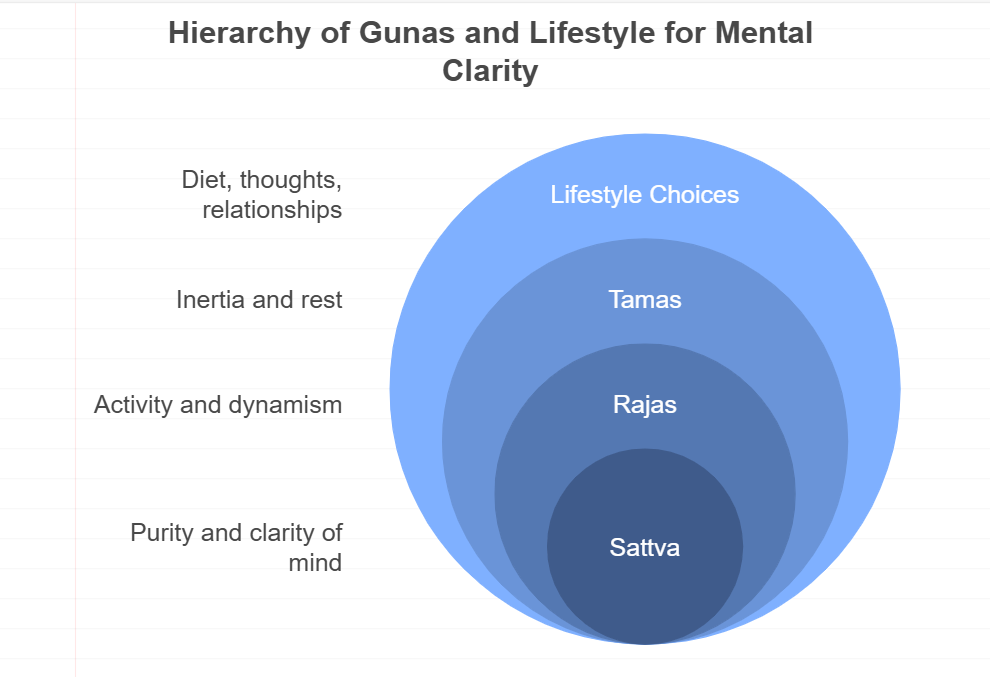
5. The Role of Sattva, Rajas and Tamas
Ayurveda also recognizes the three Gunas—Sattva (purity), Rajas (activity), and Tamas (inertia)—which influence our mental state and behavior. Striving for Sattva through a balanced diet, positive thoughts, and healthy relationships can lead to clarity and peace of mind.
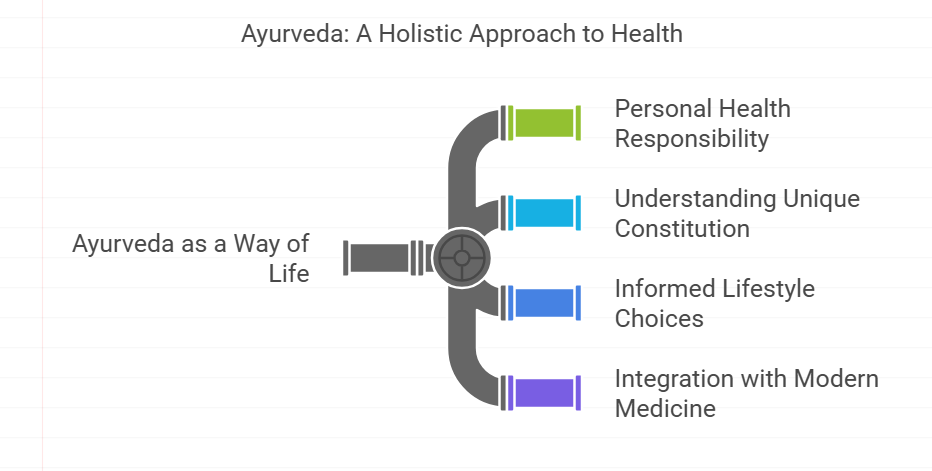
Additional Insights
Ayurveda is not just a system of medicine; it is a way of life. It encourages individuals to take responsibility for their health by understanding their unique constitution and making informed choices. Ayurvedic practices can be integrated into modern lifestyles, offering a complementary approach to conventional medicine.
Conclusion
Incorporating Ayurvedic principles into daily life can lead to profound improvements in health and well-being. By understanding the interplay of the five elements, doshas, Agni, and daily routines, individuals can cultivate a balanced lifestyle that promotes harmony within themselves and their environment. As we continue to explore the depths of Ayurveda, we uncover timeless wisdom that can guide us toward a healthier, more fulfilling life.
